Issued by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), this unique number grants permission for a business to transport regulated commodities or arrange for their transport in interstate commerce. It’s not to be confused with a USDOT number, though both are often required depending on the type of services intended to offer.
In this guide, we’ll explain what an MC number is, how it differs from other important identification numbers like the DOT number, and when a trucking company needs one. We’ll also touch on related regulatory requirements like IFTA tax compliance and FMCSA registration.
Key Takeaways
- An MC number is a requirement for many trucking companies involved in interstate commerce.MC numbers are different from DOT numbers, and both serve unique purposes.
- Some businesses may be exempt from needing an MC number.
- Getting an MC number involves registering through the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA).
- Sherpa Auto Transport ensures all carriers we work with meet regulatory requirements.
In This Guide:
- What is an MC number?
- What is an MC Number, and Why is it Important?
- What is the Difference Between MC and DOT Numbers?
- Who Needs an MC Number?
- Who is Exempt from Needing MC Numbers?
- How to Get an MC Number?
- Save Time and Money with Sherpa Auto Transport
- MC Number FAQs
What is an MC number?

An MC number, also known as a Motor Carrier number, is a unique identifier the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) assigns. It is required for companies operating as for-hire carriers—those transporting regulated goods or passengers inside and across state lines.
An MC number acts as a license that permits these businesses to engage in interstate commerce. This MC number is necessary for commercial motor carriers to operate legally and ensures compliance with federal regulations.
On the other hand, a USDOT number (U.S. Department of Transportation number) is an interstate operating authority and unique identifier assigned to a moving company performing interstate moves by the FMCSA. The government keeps track of a moving company’s safety records through this number, such as registration status, compliance reviews, ratings, inspections, crash investigations, and more.
Like the USDOT number, obtaining an MC number involves registering with the FMCSA through the Unified Registration System (URS). To apply for an MC number, one must obtain a USDOT number and complete the necessary application and registration processes.
What is an MC Number, and Why is it Important?

Simply put, the Motor Carrier (MC) number serves as a distinctive identification code the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) assigns to commercial freight carriers transporting goods across state lines. Having an MC Number is a requirement to cross state lines.
Although displaying this number on license plates is not compulsory, it must be displayed on both sides of the commercial motor vehicle (CMV) in a contrasting color when operated in interstate commerce.
Why is it Important?
Being in the trucking business, obtaining an MC number is important; otherwise, a trucking company will not be legally allowed to transport goods across state borders. Not having the proper registration could lead to hefty fines, delays, and the inability to operate.
At Sherpa Auto Transport, ensuring we comply with federal regulations, including having the necessary MC number, is key to maintaining a smooth and trusted service.
It is important to note that if goods are only transported intrastate, the federal government only requires a USDOT number. However, in case goods are being transported across state lines, an MC identification number is required to comply with federal regulations for an interstate operating authority.
Moreover, there are certain types of cargo that require specific driver’s licenses and permits in addition to the MC for trucks used in the business. For instance, a Hazardous Materials Safety Permit is required for carriers of hazardous materials, and a Household Goods Motor Carrier Permit is necessary for transporting household goods.
Note: It is also important to ensure that federal and state requirements properly insure commercial motor vehicles. Depending on the type of cargo being transported, additional permits and licenses may be required.
What is the Difference Between MC and DOT Numbers?

Usually we hear about DOT numbers alongside MC numbers, but what’s the difference?
- MC Number: Permits for hire carriers to operate across state lines while transporting regulated goods or passengers.
- DOT Number: It is required for any business operating commercial vehicles to ensure safety standards are met, even if they’re only operating within a single state.
To clarify, if operating within state lines without crossing borders, only a DOT number is required. On the other hand, an MC number is only needed for interstate operations in which the vehicle will be crossing borders from one state to another.
Sherpa Auto Transport, for instance, operates under both, ensuring we adhere to safety regulations and can legally transport vehicles across states.
Who Needs an MC Number?
An MC authority is required if someone plans to start their own trucking company and drive as an owner-operator. Independent truck drivers are allowed to operate under the MC authority of another company and do not require an MC number of their own.
Next, they must also determine what type of cargo they intend to transport: Motor Carrier of Property or Motor Carrier of Household Goods.
These two are the most commonly sought forms of MC authority. The additional types include covering brokers and international shipments of cargo. Clearly defining the operator’s role in the transportation industry is important for maintaining MC authority compliance.
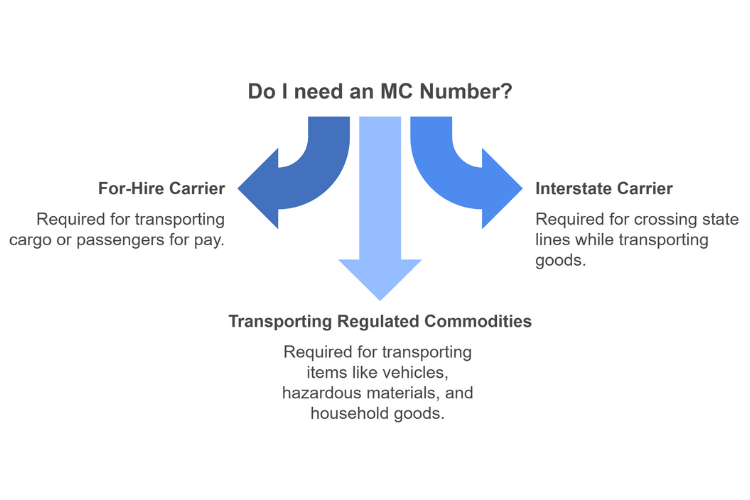
Not every trucking company will need an MC number, but many do. Here are the most common situations in which an MC number is required:
- For-hire carriers: Transporting cargo or passengers for pay.
- Interstate carriers: Crossing state lines while transporting goods.
- Transporting regulated commodities: Items considered “regulated” by the FMCSA, such as vehicles, hazardous materials, and household goods.
At Sherpa Auto Transport, our adherence to these regulations ensures that every shipment is legally compliant and our customers can trust a seamless, worry-free experience.
Who is Exempt from Needing MC Numbers?
All optional drivers don’t need to obtain MC authority. Trucking jobs that don’t require MC Authority include company (fleet) truck drivers, independent truck drivers operating under another company’s authority, and carriers operating under certain exemptions such as:
- Intrastate Carriers: Carriers operating exclusively within the borders of the state where their business is located
- Private Carriers: These carriers transport cargo belonging to their company and do not provide transportation as a service to others.
- Unregulated commodities: Certain items like agricultural products or raw materials are considered unregulated and may not require an MC number for transport.
- Carriers operating exclusively within a federally designated commercial zone: – Commercial zones located in regions where a large metropolitan area is on the border of multiple states.
- Independent Owner-Operators working for CloudTrucks: Independent owner-operators who choose to work with us drive under our authority.
How to Get an MC Number?
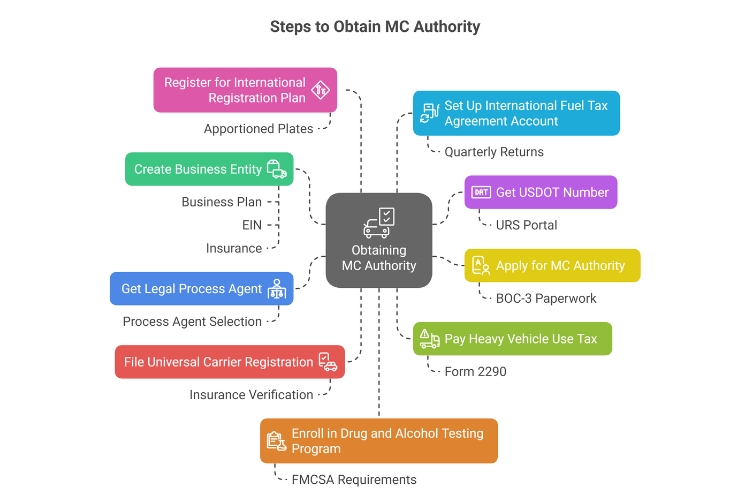
Step 1. Create a Business Entity
The first step for an MC authority application is to ensure a solid trucking business plan. The FMCSA has specific criteria, such as cargo type, operation type, and company structure. This criterion must be in sync with the business plan. The full list of criteria can be found on the FMCSA application.
Once a plan is in place, the entity will need to secure an EIN (Employer Identification Number) through the IRS and get pre-approval for liability and cargo insurance. If denied insurance later, the application for MC authority will be void.
The process can take up to 60 days. Business entity costs vary by state but typically range from $50 to $500. Depending on various factors, insurance costs range between $9,000 to $12,000 per year.
Step 2. Get USDOT Number
Before applying for an MC authority, a USDOT number is required. This can be obtained through the Unified Registration System (URS) portal. The application for a USDOT number is free of cost.
Step 3. Apply for MC Authority
Completing the process for obtaining MC authority requires filing BOC-3 paperwork through a process agent. This paperwork authorizes the process agent to accept legal documents on behalf of the trucking company in each state where the company operates. Process agents charge between $10 to $50 for filing. The FMCSA provides a list of process agents who can help.
Step 4. Get a Legal Process Agent
This step is crucial to the MC authority process. BOC-3 paperwork needs to be filed accurately through a legal process agent. They provide representation for legal documents in the states where the business operates. The cost ranges from $10 to $50, depending on the agent.
Step 5. File Universal Carrier Registration (UCR)
UCR verifies the company has active insurance in the states where the company operates. Before applying for UCR, MC and USDOT numbers are required. Skipping this step can result in severe penalties if caught operating without it. The fee for 0 to 2 vehicles is $69.
Step 6. Pay the Heavy Vehicle Use Tax (HVUT)
If driving a heavy vehicle, paying the HVUT is required for all heavy vehicles operating on public highways. To do this, fill out and submit Form 2290 to the IRS. The tax amount owed depends on the cargo and where it’s been transported.
Step 7. Register for an International Registration Plan (IRP)
The IRP is a state and Canada agreement allowing carriers to conduct interstate transport, commonly called “apportioned plates”. IRP registration is necessary to set up an IFTA account—costs for IRP registration fees range from $1,500 to $2,000 per vehicle.
Step 8. Set Up an International Fuel Tax Agreement (IFTA) Account
Like the IRP, the IFTA agreement between states and Canada ensures that fuel taxes are collected properly. Filing quarterly returns with the company’s home state is required to stay compliant. Some states have additional permit requirements.
Step 9. Enroll in a Drug and Alcohol Testing Program
Finally, before hitting the road, the FMCSA requires all CDL drivers to enroll in a drug and alcohol testing program. These programs have strict rules covering substances tested and the frequency of tests. Be sure to follow the FMCSA’s instructions to comply with their requirements.
Save Time and Money with Sherpa Auto Transport

At Sherpa, we make it easy to ship your car across the country. As a broker, we do all of the heavy lifting. As part of our thorough vetting process, we review all regulatory records of prospective carriers. Only the best carriers have a chance to transport our customers’ vehicles.
MC Number FAQs
Can You Have a DOT Number Without an MC Number?
You can have a DOT number without an MC number if your business does not cross state lines or transport regulated goods. A DOT number ensures your fleet meets safety standards, but the MC number is only required for interstate commerce.
Do You Need an MC Number to Run Local?
You typically only need an MC number if operating within state lines and dealing with unregulated goods. However, you may still require a DOT number depending on the size and type of vehicles you utilize.
How Much Do DOT and MC Numbers Cost?
The fee for registering an MC number with the FMCSA is $300. There is no cost for obtaining a DOT number, but your business may need to meet specific state regulations, which could incur additional fees.
Can I Operate While Waiting for My MC Number?
You can legally operate as a for-hire interstate carrier once your MC number has been issued and active. Operating without the necessary approval can lead to fines and delays in your operations.
Do I need an MC Number for intrastate transportation?
You don’t need an MC Number to operate your vehicle intrastate. An MC Number is only required if you transport your carriers across the state lines.
How long does it take to obtain an MC Number?
Normally, FMCSA issues MC numbers within 24 hours. However, an MC Number takes around 20 to 25 days to get activated. This is because all the new MC Numbers issued by FMCSA have to go through the protest period before they get activated.
Can I check the status of my MC Number application online?
Yes, to check the status of your MC Number online, you will need to go to the Safety and Fitness Electronic Records (SAFER) system online. Under the heading, FMCSA searches, click on Licensing and Insurance. Then, enter your MC number or USDOT number and click search.
How often do I need to renew my MC Number?
Your MC Number must be updated every two years, according to the guidelines provided by FMCSA.







